Arthrosis of the knee joint (also known as gonarthrosis) is a fairly common disease that has recently been found not only in the elderly but also in the young.
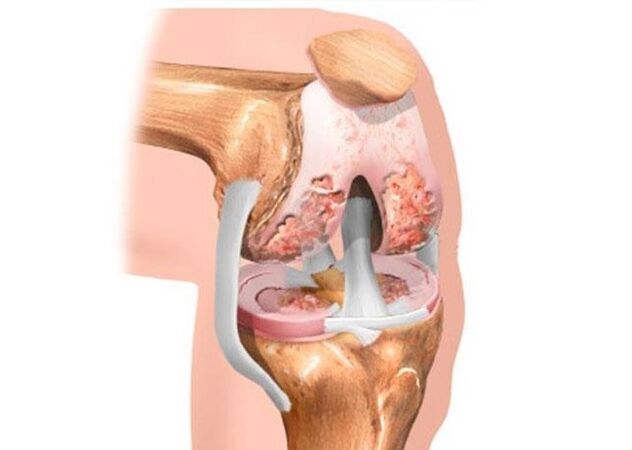
Pathology is one of the main causes of a patient’s disability if they refuse to seek help from a traumatologist or orthopedist.
Let’s look at why patients develop gonarthrosis of the knee joint, what the main signs are, how dangerous it is, and how effectively progressive knee destruction is treated.
The main factors in the appearance of pathology
The joints are constantly subjected to significant stress. The knee is particularly affected: they are forced to do significant physical work and therefore wear out quickly. The deformation process is exacerbated by the fact that the legs are forced to bear the weight of the body.
This fact further contributes to the fact that the knees begin to wear out, the cartilage tissue of the joint thins and breaks down.
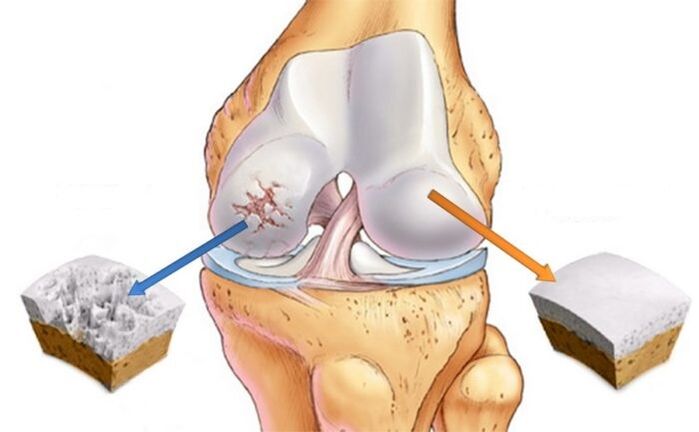
The following causes can accelerate the pathological process in the joints:
- Increased body weight in patients. The complete destruction of the joint is much faster and more intense. The disease in question has been shown to be three times more common in obese people than in those of normal weight.
- Intense exercise, which causes constant damage to the joints.
- Frequent fractures and previous knee injuries contribute to the degeneration of articular cartilage at a very young age.
- Anomalies in the location of bones - the so-called valgus or varus deformity.
- Poor development of the ligament apparatus of the knee leads to frequent injuries and dislocations. Due to the lesions described, the patient develops arthrosis.
- Damage to the meniscus triggers a degenerative process of knee destruction.
- Constant stress leads to a deterioration in the health of the musculoskeletal system.
- Disruption of metabolic processes in the body due to a lack of nutrients and minerals (bones suffer the most from calcium deficiency).
In addition, the following persons are included in the risk group:
- all athletes;
- patients who have reached the age of 50, regardless of gender;
- women who have started menopause;
- patients with varicose veins;
- persons with an unfavorable inheritance.
What are the degrees of the disease
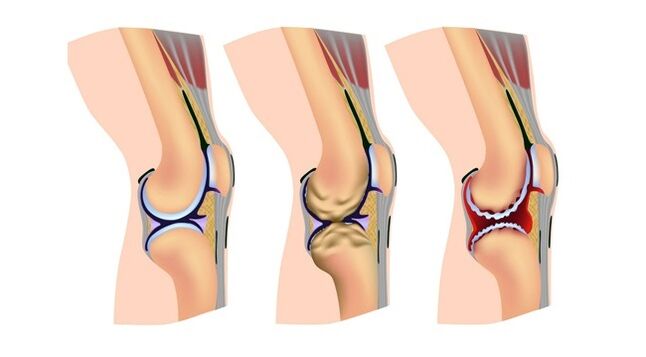
The pathology in question develops gradually, very slowly. At first, it may not appear and the patient may not rush to the doctor. Nevertheless, the pathological process has already begun, and if not stopped in time, the functions of the lower extremities are gradually lost, leading to the development of disability.
Thus, in Grade 1, the patient may notice that their legs are tired, even if the load was small. Some restriction on the mobility of the knee joint is noticeable, and significant cracking is heard during movement.
There are pronounced onset pains when the discomfort does not provide peace, especially in the morning. After the "distribution" of the patient, the discomfort gradually decreases and increases again after sports activities. At this stage in the development of the disease, there is no pronounced deformation in the bone tissue.
In grade 2, the pain increases. Because of this, walking is impeded. Sometimes it becomes almost impossible for the patient to move normally, and even after a light load, a long rest is required. As the joint gap narrows, osteophytes grow on the bones and abnormal fluid accumulates in the joint.
In grade 3, the pain occurs not only during work and sports, but also in complete peace of mind. The deformity of the knee is very pronounced, which makes any movement difficult.
Common symptoms of the disease
The general symptoms of arthrosis of the knee joint should be noted:
- Pain. It doesn’t show up suddenly, but the mild discomfort can last for almost years. More severe pain is caused by trauma.
- Deformity of the knee (retains its former shape).
- Accumulation of fluid in the intraarticular cavity. If the amount exceeds certain values, a so-called Baker cyst is formed. A tight, flexible object appears on the back of the knee. It is most noticeable when the joint is stretched.
- Knee rupture is observed when the pathology is in the second, third stage. It is significantly different from what is observed in a healthy person when the knee is bent or stretched. The sound feels rough and painful. Sometimes the crackling interferes with active movements.
- Decreased normal range of motion in the joint. Usually the patient is unable to bend, unfold the affected leg. Able to bend at right angles, further movements are accompanied by severe pain.
- Knee stiffness occurs primarily in stage 3. Sometimes patients can only walk on bent limbs.
- Increased pain when the weather changes.
- Significant thinning of cartilage. In advanced cases, bone exposure is sometimes observed. X-rays of the knee show a significant accumulation of osteophytes.
Types of arthrosis
Depending on the origin, arthrosis is primary (occurs as a separate disease) or secondary - a complication of existing pathologies. Depending on the location of the localization, the pathology is right, left, and bilateral.
Based on the characteristics of the manifestation, the following types of disease are distinguished.
- Deforming arthrosis is characterized by a chronic course, irreversible changes in the joint.
- Patellofemoral arthrosis is caused by prolonged intense physical exertion.
- Inflammatory arthrosis occurs due to a prolonged, untreated inflammatory process in the joints.
- Dysplastic arthrosis is caused by congenital anomalies in the structure of the knee joint.
- Post-traumatic arthrosis occurs due to frequent injuries to the musculoskeletal system.
- Metabolic arthrosis occurs in gout and other metabolic disorders.
- Post-infection arthrosis is a consequence of improperly treated inflammatory pathologies.
- The static form of the disease is detected when the knee is constantly under increased pressure.
- If the cause of the knee lesion is not determined, experts talk about idiopathic arthrosis.
Characteristics of the treatment of the disease

Rheumatologists and traumatologists are involved in the early stages of the disease. If you have gone too far, the patient should see a surgeon. Finally, some clinics have a tight specialist who deals with joint diseases - an arthrologist.
The range of therapeutic measures depends on the extent to which the disease has progressed. If the cause of the pathology in question is eliminated at an early stage, almost permanent cure can be achieved.
The goal of any therapy is to completely eliminate the pain, restore the destroyed cartilage, and increase the range of active movements in the joint.
The course of medication is selected exclusively by a doctor. The patient should not prescribe these to themselves as this may contribute to further damage to the joint. The main medicines are prescribed:
- Non-steroidal anti-inflammatory tablets or ointments. Their activity is to relieve pain and inflammation in the affected area. Sometimes injections can be prescribed into the joint cavity.
- Products that improve blood circulation in the knee. These are muscle relaxants, antispasmodics. The latter relieves pain well.
- Products that restore articular cartilage improve normal nutrition.
Novocaine blockade helps relieve acute pain. The injection can be given from the outside or inside of the joint. The easiest and safest method is to administer the drug from the outside. With proper manipulation, the pain goes away almost immediately.
An ointment based on strong NSAIDs also helps cope with pain. It should be remembered that strong medicines should not be used for a long time. Any medication, even the most effective one, can have side effects and cause allergic reactions. This means that self-treatment of this serious illness is categorically not allowed.
Conservative treatment can be effective, provided the disease has not gone too far. Surgery is recommended in case of irreversible joint damage. A metal prosthesis is implanted.
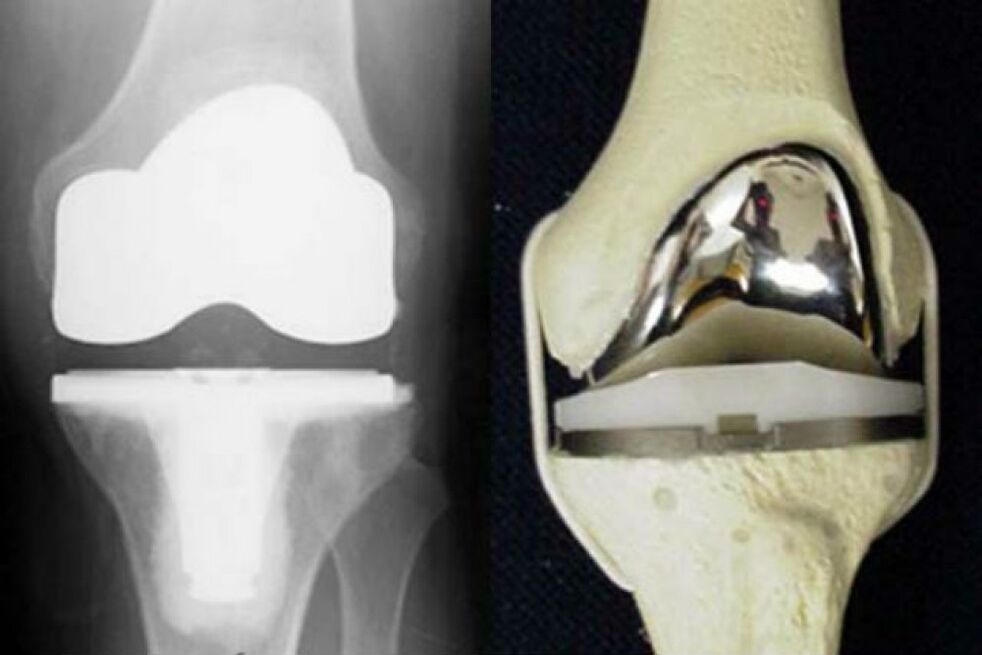
Currently, this is the only way to restore knee mobility. The disadvantage of these operations is the limited life of the prosthesis, the high price.
In arthroscopy, all surgical procedures are performed by microscopic puncture in the joint. During surgery, the affected cartilage pieces, blood clots, etc. are removed from the joint. In stage 3 of the disease, an intervention of the type described is ineffective.
Periarticular osteotomy is used to reduce the load. It has been shown to be performed when the joint is not yet completely destroyed.
Sticks and orthoses are used to relieve the joint affected by the degenerative process.
The duration of treatment for the disease depends on a number of factors. Therapy with chondroprotectors can be quite long - six months or more, as their effects are rather slow. A qualified healthcare professional can determine how long you should take the medication you are prescribed.
Use of chondroprotectors in the treatment of arthrosis
Doctors prescribe non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs (NSAIDs) to relieve pain.
However, even the new generation of NSAIDs cannot prevent the spread of the pathological process. Chondroprotectors are increasingly used to reduce the intensity of joint degeneration and restore normal mobility.
Modern medicines in this group help to repair joint tissue. This is due to the content of chondroitin in them. It is a natural component of cartilage tissue. Constant intake of drugs belonging to this group helps to restore and improve health.
Despite the wide range of medications, only the doctor can decide which is right for the patient. Chondroprotectors injection is not presented by everyone, the drugs themselves are diluted in special solvents.
Dietary supplements should be taken if the patient is following a balanced diet and is taking other joint support medications.
The role of movement therapy and physiotherapy in the treatment of gonarthrosis
With the described pathology, the patient is categorically contraindicated in a supine lifestyle. Physical activity in any disease of the musculoskeletal system is simply necessary for all categories of patients. Of course, it must be dosed; all exercises are performed under the supervision of a physician only.
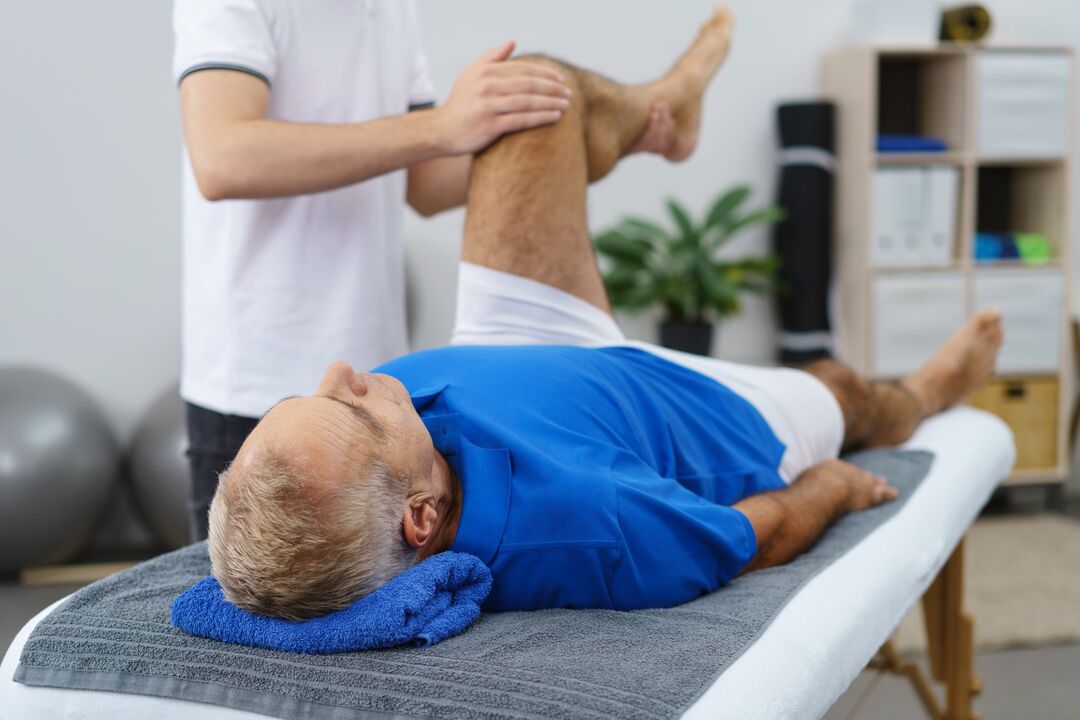
Special practices are individually selected by the traumatologist or rehabilitation therapist for each patient. There is no need to think that the different sets of classes available on the Internet are suitable for all patients without exception.
They can be really beneficial to some, while they do great harm to others. All loads should be gentle, with the goal of restoring the functions of the affected joints as quickly and completely as possible.
At home, it is recommended to do a simple exercise: while lying down, raise your legs, hold for a few minutes, then lower. It is harmless and can even be done by patients with the third stage of the disease. Exercises are given to stretch the joint capsule under the supervision of a doctor. But if it causes pain, execution should be stopped immediately.
The physiotherapeutic methods of treating the disease are as follows:
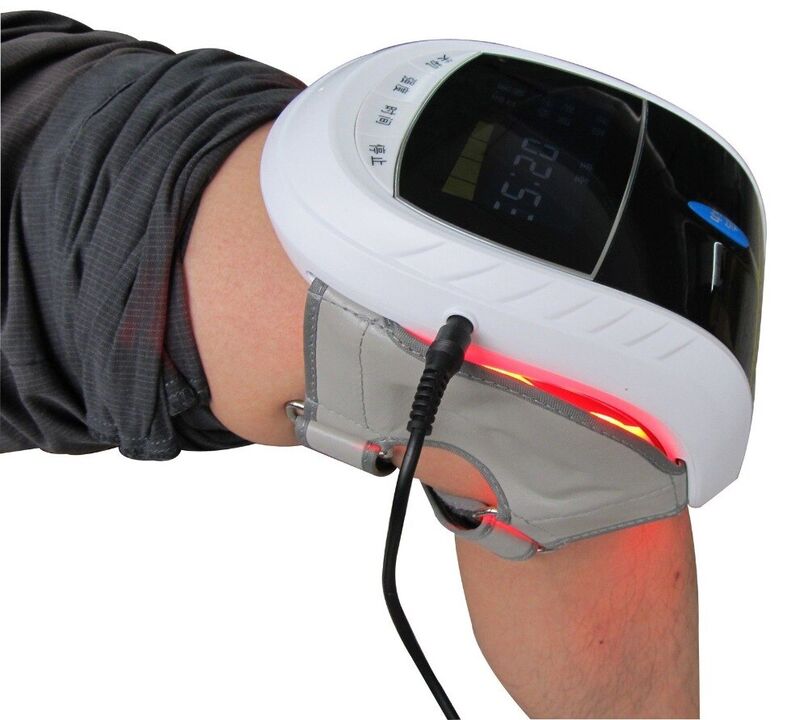
- massage (strictly forbidden without a medical statement);
- manual therapy (should be as gentle as possible, does not cause discomfort);
- medical laser treatment;
- effect on reflexogenic points using the finest needles;
- hot or cold treatment (again, no heat treatment is required at home);
- magnetic field treatment;
- phonophoresis;
- electrophoresis;
- paraffin therapy;
- ozokerite treatment;
- with moxibustion.
Nutrition for gonarthrosis
Adequate nutrition is the basis for the successful treatment of degenerative diseases of the musculoskeletal system. An improperly formulated diet can cause the patient to gain weight. Lack of vitamins and microelements aggravates the course of the pathology.
Every person with gonarthrosis should increase the amount of foods fortified with vitamins and minerals in their daily diet.
Nutrition experts recommend that you closely monitor the caloric content of foods. Fasting or extreme diet is strictly prohibited. They can be harmful, gaining weight even more.
It is important that the breakfast is balanced. You should eat at least five times a day. It is recommended to use fruit and bread for snacks.
The following foods and meals are excluded:

- sweet soda;
- fatty foods;
- half-done products;
- spices;
- foods containing flavor enhancers;
- fatty meats;
- fried foods;
- White cabbage;
- tomatoes and bell peppers;
- orange, lemon;
- chocolate;
- bananas, grapes (very high in calories).
Jelly meat and jelly are useful. They contain large amounts of collagen, which allows the bone to recover. Jelly meat is prepared to contain less fat, thus reducing its caloric content.
Sources of protein in people with osteoarthritis can be dairy products - cheese, cottage cheese or kefir. It is very useful to consume legumes. Be sure to include nuts in your diet.
It is necessary to adhere to the drinking system. Considering that there are no related kidney diseases, it is recommended to consume about 2 liters of water.
Alternative treatments for the disease
It should be recalled that traditional methods are not a substitute for effective methods of formal medicine. And therefore they must be used in a complex treatment, there can be no other therapy for this serious disease.
Use regular soda to relieve knee swelling. The material is moistened with baking soda and wrapped around the knee. It is advisable to attach a plastic bag above to increase the heat effect. Keep the prepared compress all night long.
They make a similar compress by adding edible vinegar. Acetylsalicylic acid tablets should be taken in parallel with compression.
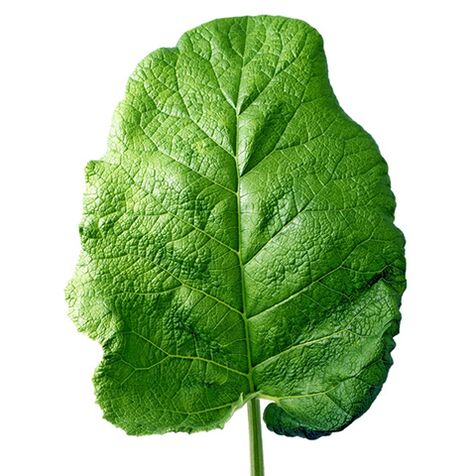

The leaves of burdock are very useful for the knee. It is advisable to lubricate the knees with vegetable oil before applying the leaves. It is necessary to have several layers of leaves.
All this is packed in a plastic bag. The birch leaf is also wrapped in the same way.
Medical bile is good for relieving inflammation, swelling and pain. It is used in the form of a night warming compress. Bile has virtually no side effects.
Treatment with honey is performed in cases where the patient is not allergic to it. After the aching joint has been warmed up with a heating pad, it should be smeared with honey and a gentle massage should be performed. Then fasten the leaves of the burdock to your knees.
Prevention of gonarthrosis
Preventing a disease is much easier than curing it. The preventive measures are as follows:

- a high-quality, balanced diet using adequate amounts of protein, vitamins and calcium;
- elimination of bad habits;
- the fight against obesity;
- normalization of physical activity;
- prevention of joint injuries during sports or strenuous physical work.
When the first signs of trouble appear, it is important to see a doctor immediately. You can find out which doctor is treating your gonarthrosis during a clinical consultation. It is advisable to undergo a comprehensive medical examination to find out the cause of the disease.
Inflammation of the knee joint is a serious illness: if ignored, there is a risk of disability and complete immobility. To prevent this, the affected joint must be treated properly. Therapeutic measures started early contribute to the almost complete remission of this pathology, contribute to the maintenance of high performance and quality of life.



















